Introduction
If you’ve heard about Bitcoin, cryptocurrency, or Web3, then you’ve probably also come across the word blockchain. But many beginners still ask the same question:
What is blockchain, and why is everyone talking about it?
Blockchain is one of the most important digital innovations of our time. It is changing how we store data, transfer money, and build trust online.
In this guide, we’ll explain what blockchain is, how it works in simple steps, and why it is a revolutionary technology beyond crypto.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a digital system for recording information in a way that makes it extremely difficult to change, hack, or manipulate.
In simple words:
Blockchain is like a digital notebook that stores records permanently and transparently.
Instead of being stored in one place (like a traditional database), blockchain data is stored across a network of computers, making it decentralized and secure.
Why is it Called “Blockchain”?
The term blockchain comes from two words:
- Block → A container that stores data or transactions
- Chain → A connection between blocks in correct order
Each block is linked to the previous one, forming a secure chain of information.
That’s why it’s called a blockchain.
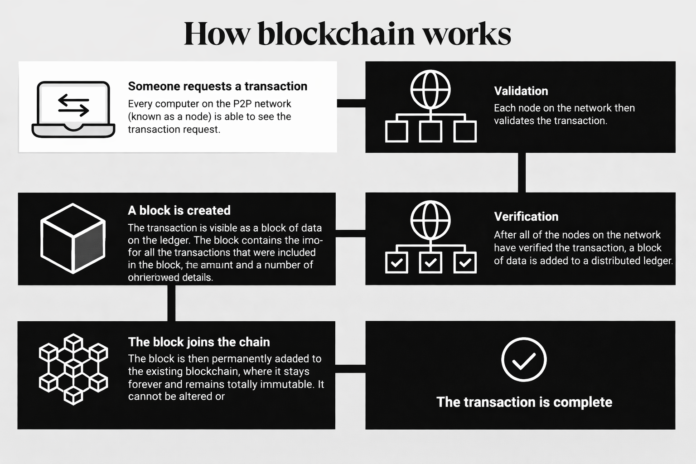
How Does Blockchain Work? (Step-by-Step)
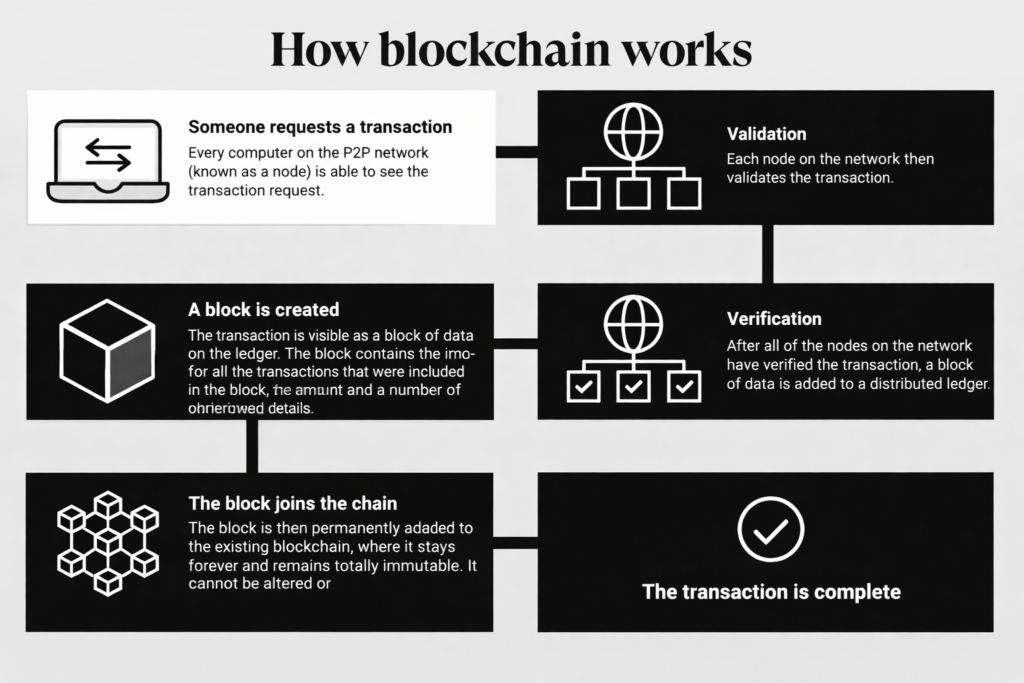
Let’s break down how blockchain works in the simplest way.
Step 1: A Transaction Happens
A transaction could be:
- Sending cryptocurrency
- Recording ownership
- Sharing data
- Making payments
Example: You send Bitcoin to a friend.
Step 2: The Transaction is Shared with the Network
The transaction is broadcast to a global network of computers known as nodes.
Each node has a copy of the blockchain.
Step 3: Verification Takes Place
Before the transaction is added, the network checks:
- Is the transaction valid?
- Does the sender have enough balance?
- Is it correctly signed?
This verification is done using consensus mechanisms like:
- Proof of Work (PoW)
- Proof of Stake (PoS)
Step 4: A Block is Created
Once verified, the transaction is grouped with others into a block.
A block contains:
- Transaction data
- Timestamp
- Unique hash code
- Previous block’s hash
Step 5: The Block is Added to the Chain
The new block is added to the blockchain permanently.
Once added, the information becomes almost impossible to change.
Step 6: Transaction Becomes Permanent
Now the transaction is recorded forever, visible to everyone, and secure from tampering.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is special because it offers features that traditional systems cannot.
1. Decentralization
Blockchain is not controlled by one company or government.
It works on a distributed network of computers.
2. Transparency
Every transaction is recorded publicly, meaning anyone can verify it.
This builds trust in the system.
3. Immutability
Once a block is added, it cannot be changed easily.
This makes blockchain highly reliable for record-keeping.
4. Strong Security
Blockchain uses cryptography to protect data, making hacking extremely difficult.
5. Trust Without Intermediaries
Blockchain allows peer-to-peer transactions without needing:
- Banks
- Middlemen
- Central authorities
Types of Blockchain
There are different kinds of blockchains depending on use case.
Public Blockchain
- Open to everyone
- Fully decentralized
- Example: Bitcoin and Ethereum
Private Blockchain
- Controlled by a single organization
- Used by businesses
Consortium Blockchain
- Controlled by a group of organizations
- Semi-decentralized
Hybrid Blockchain
- Mix of private and public features
Blockchain vs Traditional Database
| Feature | Blockchain | Traditional Database |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Decentralized | Centralized |
| Transparency | High | Low |
| Data Editing | Very difficult | Easy |
| Security | Very strong | Moderate |
| Trust | Built-in | Requires third party |
Real-Life Uses of Blockchain (Beyond Crypto)
Blockchain is not just about cryptocurrency. It is already being used in many industries.
1. Digital Payments
Crypto transactions are powered by blockchain.
2. Supply Chain Tracking
Companies track products from origin to delivery.
3. Healthcare Records
Patient records can be stored securely and privately.
4. Voting Systems
Blockchain can make elections transparent and tamper-proof.
5. NFTs and Digital Ownership
NFTs prove ownership using blockchain.
6. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Blockchain enables lending, borrowing, and trading without banks.
Advantages of Blockchain
Blockchain offers many benefits:
✅ Secure digital transactions
✅ Removes intermediaries
✅ Reduces fraud and corruption
✅ Improves transparency
✅ Faster global payments
Limitations of Blockchain
Like any technology, blockchain has some challenges:
- Scalability issues
- High energy usage in some networks
- Complexity for beginners
- Regulatory uncertainty
However, improvements are happening every year.
Is Blockchain the Future?
Yes, blockchain is considered one of the core technologies of the future.
It will power:
- Web3 internet
- Digital identity
- Tokenized assets
- Decentralized applications
- Global financial systems
Conclusion
So, what is blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records information securely, transparently, and permanently. It is the foundation of cryptocurrency but also has the potential to transform industries like finance, healthcare, and data security.
Understanding blockchain is the first step toward understanding the future of digital technology.
- ✅ Internal Link 1
- Learn more about blockchain technology basics (link)
- ✅ Internal Link 2
- Explore our beginner article on blockchain concepts (link)
- ✅ Outbound Links (Authority Sources)
- Blockchain explained by IBM
https://www.ibm.com/topics/blockchain - Official Bitcoin Website
https://bitcoin.org
Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only. It does not provide financial or investment advice.